gas analysis on gc|gas chromatography quality control : agencies Gas chromatography (GC) is an analytical methodology, which was devised by Nobel Laureate, Martin, et al. in 1952. More than 60 years after the award, GC systems are widely . 25 de fev. de 2020 · Fox. O site da FOX permite mais que o acesso a futebol online. Como diferencial, o site permite o acesso a todos os canais gerenciados pela empresa. Para assistir as partidas de futebol de campeonatos como a Libertadores, Copa Sul-Americana, Espanhol e Alemão. É possível contratar o serviço, em média por R$ 34.90, dentro dos .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBMEGA HOME – Encuentra todo lo que necesitas para tu hogar en Mega Shop: ¡decora y equipa tu espacio con elegancia y funcionalidad! Encuentra todo lo que necesitas para .
A Practical Gas Analysis by Gas Chromatography provides a detailed overview of the most important aspects of gas analysis by gas chromatography (GC) for both the novice and expert. Authors John Swinley and Piet de Coning provide the necessary information on the selection .
Gas chromatography (GC) is an analytical technique used to separate and detect the chemical components of a sample mixture to .The method is the collection of conditions in which the GC operates for a given analysis. Method development is the process of determining what conditions are adequate and/or ideal for the analysis required. Conditions which can be varied to accommodate a required analysis include inlet temperature, detector temperature, column temperature and temperatur.Gas chromatography (GC) is an analytical methodology, which was devised by Nobel Laureate, Martin, et al. in 1952. More than 60 years after the award, GC systems are widely .According to the state of the stationary phase, gas chromatography can be classified in gas-solid chromatography (GSC), where the stationary phase is a solid, and gas-liquid chromatography (GLC) that uses a liquid as stationary .
When hydrolyzed, the surface of a diatomaceous earth contains silanol groups (–SiOH), that serve as active sites for absorbing solute molecules in gas-solid chromatography (GSC). In gas-liquid chromatography (GLC), we .Learn about the fundamentals of gas chromatography (GC). This overview explains the basic principles of gas chromatography and the key components of a gas chromatograph, including the GC inlet, GC column, and GC detector. Gas chromatography is one of the sole forms of chromatography that does not utilize the mobile phase for interacting with the analyte. The stationary phase is either a solid adsorbant, termed gas-solid chromatography .
the first gas chromatography
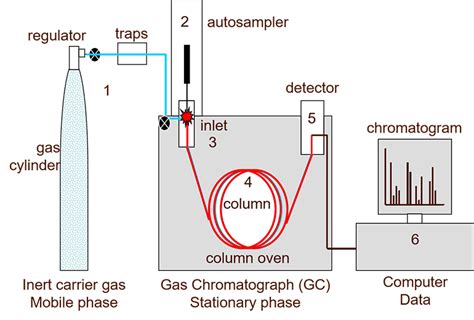
Gas chromatography (GC) is an analytical technique applicable to gas, liquid, and solid samples (components that are vaporized by heat). If a mixture of compounds is analyzed using GC . QUANTtitative Analysis. Quantitative analysis tells us how much of an analyte is in a mixture. In an ideal GC or GC-MS analysis, the peak height and area under the peak are proportional to the amount of analyte injected . Gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC/MS) analysis is an effective testing and troubleshooting tool for many manufacturers across industries, helping identify and quantify the materials that make up a sample . Image 1: The image above shows how a gas chromatograph looks like. Picture Source: hiq.linde-gas.com It is a term used to describe analytical separation methods used to check volatile substances in their gas phase. .
Fundamentals of Gas Chromatography APPLICATION NOTE OIL & GAS Figure 1 - The Functional Components of a Gas Chromatograph Overview Gas chromatography is one of the most widely used techniques for analyzing hydrocarbon mixtures. Some of the advantages of . As the analysis valves are located inside the oven compartment,
Table 27.4.1 . Representative Applications of Gas Chromatography; area applications; environmental analysis: green house gases (CO 2, CH 4, NO x) in air. pesticides in water, wastewater, and soil. vehicle emissions. trihalomethanes in drinking water. clinical analysis: drugs. blood alcohols. forensic analysis: analysis of arson accelerants .The range of GC detectors available, combined with expertise from senior laboratory staff, ensure quality service. Gas chromatography techniques: Gas Chromatography [GC] Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Analysis [GCMS] High Resolution GCMS [GC/MS/SIM/HR] Gas Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectroscopy [GC-MS-MS]Single quadrupole GC-MS. When gas chromatography is combined with a mass spectrometer that includes just one quadrupole, it is often referred to simply as GC-MS. GC-MS is well suited to the everyday analysis of samples where either targeted or untargeted analysis is required as these systems can be operated using either targeted selected ion monitoring (SIM) or .What is Gas Chromatography? (GC) Gas chromatography (GC) is an analytical technique applicable to gas, liquid, and solid samples (components that are vaporized by heat). If a mixture of compounds is analyzed using GC system, each compound can be separated and quantified. 2.1. Overview of GC Analysis
Analysis of Permanent Gases Sample Introduction –Syringes and valves General discussion on PLOT columns The molesieve column is at the heart of permanent gas separations Techniques when CO 2 + C 2’s, C 3’s, etc. is also needed Column Isolation Parallel columns Cryogenic separations Unique selectivity packed columns Gas chromatography, in analytical chemistry, technique for separating chemical substances in which the sample is carried by a moving gas stream through a tube packed with a finely divided solid that may be coated with a film of a liquid. Because of its simplicity, sensitivity, and effectiveness incarrier gas. When using hydrogen as the carrier gas, try an initial average linear velocity of 60 cm/sec. If better resolution is desired, reduce the velocity to no less than 50 cm/sec; however, the analysis time will be increased. If a shorter analysis time is desired, increase the velocity to 70 cm/sec and 80 cm/sec. Be
Example of a GC–MS instrument. Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) is an analytical method that combines the features of gas-chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify different substances within a test sample. [1] Applications of GC–MS include drug detection, fire investigation, environmental analysis, explosives investigation, food and flavor .Gas chromatography (GC) is a powerful analytical technique that separates and analyzes compounds in a gas phase. The instrument used for this process consists of a sample injector, a column where separation occurs, a detector to measure compound concentrations, and a data recording system. Gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS) is an analytical technique that combines two powerful techniques; gas chromatography and mass spectrometry and is used to separate, identify, and quantify volatile compounds. It is therefore perfect for analyzing the many relatively low molecular weight compounds. Although it can be used with solid, gaseous, and .
The choice of carrier gas for GC-TCD analysis depends upon the sample compounds. Sensitivity for a compound increases when there is a larger difference in thermal conductivity between the carrier gas and that particular compound. Typically, helium is used because of its large difference in thermal conductivity compared to most compounds. However,•Fig. 2: Chromatogram of the flue gas calibration gas mixture 3 Proprietary & Confidential Figure2. GC chromatogram of the flue gas components. Table 2. Repeatability results of the reference gas standard mixture. Area Repeatablity of Flue Gas Test Mixture Analysis on TRACE 1100 GC Analyzer with Valve Oven Group Sample name File name CO 2 O 2 .The analysis of permanent gases using the Agilent 6820 equipped with a single filament Thermal Conductivity Detector is described. For these applications, the Agilent 6820 gas chromatography system was configured with a gas sampling valve, isolation valve, and purged-packed inlet. Agilent Cerity for Chemical QA/QC was used to con-
Quantitative Analysis. In a GC chromatogram, the size and area of the component peak are proportional to the amount of the component reaching the detector. . of changes in sample composition when introduced to a gas chromatograph. Disadvantages:Extra work is required to add the target component to the unknown sample. Because a target .for Gas Chromatography Analysis Francis Orata Masinde Muliro University of Science and Technology, Kenya 1. Introduction Derivatization reactions are meant to transform an analyte for detectability in Gas Chromatography (GC) or other instrumental analytical methods. Derivatization in GCThe saturate fraction is analyzed by gas chromatography, leading to n-alkanes content. Aromatics are analyzed by Gas Chromatography with Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). Resins and asphaltenes are the most difficult to analyzed by GC because of their high boiling points. Therefore, the applications of GC on the analysis of heavy oil, which has a high
Carrier Gases in Capillary GC Analysis. CARRIER GAS Mobile Phase •Carries the solutes down the column •Selection and velocity influences efficiency and retention time •Must be inert to solutes and stationary phase . GC. CARRIER GAS Flow Rate (mL/min) "Volume" Measurement: • At column exit
1.1. Overview of GC Analysis. Gas chromatography (GC) is an analytical technique applicable to gas, liquid, and solid samples (components that are vaporized by heat). If a mixture of compounds is analyzed using GC system, each compound can be separated and quantified.The gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) interface is the section of the instrument starting at the column exit in the gas chromatograph and extending to the entrance to the ion source of the mass spectrometer. . For GC-MS analysis of 5-mC, DNA is often hydrolyzed using formic acid and the resulting nucleobases are then derivatized .The thermal conductivity detector (TCD) is a universal detector for gas chromatography that responds to virtually any compound, excluding the carrier gas. It is generally used for the GC analysis of permanent gases, light hydrocarbons, and compounds that do not respond well to a flame ionization detector (FID). Gas-phase samples are already in the state in which GC separations occur, therefore, there is no need for further transformation. Some gas-phase samples must be sampled in situ, for example air, breath from a patient or air from a processing plant.For others, a large sample can be taken and then a portion of this analysed, for example a cylinder of industrial .
Gas Chromatography (GC) is a fundamental analytical technique that plays a pivotal role in modern scientific research and industry. With its remarkable ability to separate and quantify complex mixtures of volatile and semi-volatile compounds, GC has earned a prominent place in fields ranging from environmental analysis to pharmaceutical development.Gas chromatography is a method using gas as the mobile phase. Gas chromatography-mass spectometry (GC-MS) is generally used for qualitative and quantitative analysis and determination of resveratrol. Gas chromatographyfeatures high sensitivity and accuracy, simple and rapid operations, and low sample consumption, but the sample pretreatment is .
how to use a gas chromatography
gaussian gas chromatography
packaging compression test
WEBVerónica Domingues is on Facebook. Join Facebook to connect with Verónica Domingues and others you may know. Facebook gives people the power to share and makes the world more open and connected.
gas analysis on gc|gas chromatography quality control